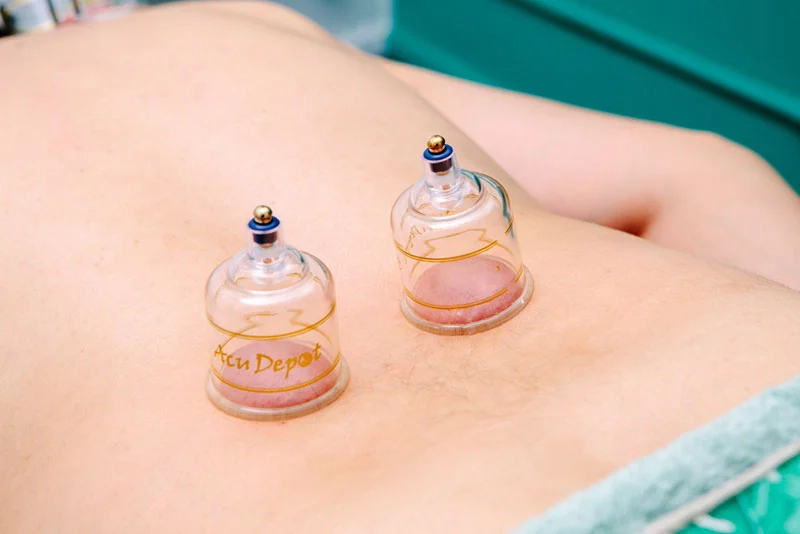
Cupping therapy, often simply called “cupping,” is a traditional healing practice that has roots in ancient civilizations, including Chinese, Egyptian, and Middle Eastern cultures. It has gained more visibility in recent years, partly due to high-profile athletes and celebrities endorsing its benefits. This article explores the uses of cupping therapy, delves into its purported benefits, and examines the scientific evidence behind its effectiveness.
Understanding Cupping Therapy
Definition and Techniques
Cupping therapy is an alternative therapeutic practice where cups are placed on the skin to create suction. Dry cupping involves simply suctioning the cups to the skin, while wet cupping may involve making small incisions in the skin to draw blood out during the suction process.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Historically, cupping was used to treat a range of ailments and conditions from muscle pain and stiffness to respiratory disorders. Its use in traditional Chinese medicine is often associated with the belief in balancing qi (chi), the life force. In Middle Eastern regions, it has been a common practice in prophetic medicine.
Applications of Cupping Therapy
Pain Management
One of the most common uses of cupping therapy is to manage pain, including that caused by conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia, as well as muscle pains and spasms. The suction created by the cups is believed to promote blood flow, which can help reduce muscle tension and promote cell repair.
Sports Recovery and Performance
Many athletes use cupping as a tool to enhance recovery and improve performance. The theory is that the increased blood flow helps relieve muscle soreness and accelerate the healing of sports injuries. Notable athletes, including Olympic swimmers and professional football players, have been seen with the characteristic circular bruises left by the cups.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging
Cupping is also touted to improve skin health by promoting blood flow and relieving skin inflammation. Some advocates claim that it can also help with acne and eczema, as well as provide anti-aging benefits by improving elasticity and reducing puffiness.
Respiratory Conditions and Immunity
Cupping has traditionally been used to treat respiratory conditions such as bronchitis and asthma. The suction is thought to help open the lungs and improve circulation, which could theoretically aid in expelling phlegm. Furthermore, boosting blood flow can improve immune function, potentially helping the body fight off pathogens.
Scientific Evidence: Does Cupping Really Work?
Review of Studies
The scientific community remains skeptical about cupping due to a lack of high-quality, conclusive studies. Most existing research comprises small-scale studies, anecdotal evidence, or studies with significant methodological flaws. However, some studies suggest modest benefits in pain relief and muscle relaxation.
Analysis of Benefits vs. Placebo Effects
Determining whether the benefits of cupping are due to the procedure itself or are a result of placebo effects is challenging. Placebo effects are powerful and can lead to significant improvement in symptoms, particularly in treatments like cupping, where the experience and expectations of the therapy play a significant role.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While cupping is generally considered safe when performed by trained professionals, it does carry some risks. These include mild discomfort, burns (from heated cups), bruises, and in rare cases, skin infection. It’s crucial for practitioners to use sterile equipment and follow proper techniques, especially during wet cupping.
Expert and Practitioner Perspectives
Medical Professional Skepticism
Many medical professionals are skeptical of cupping due to the lack of solid evidence and the risks involved. They advocate for more rigorous clinical trials to better understand the therapy’s effects and its safety.
Alternative Medicine Advocacy
Practitioners of alternative medicine, however, often share positive experiences and advocate for cupping as a supplementary treatment, especially for pain and relaxation. They argue that the lack of negative side effects, when done correctly, makes it a viable option for those seeking alternative or holistic treatment methods.
Conclusion: Evaluating the Usefulness of Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy remains a popular but controversial practice. While there is some anecdotal evidence and preliminary research supporting its benefits, particularly for pain management and sports recovery, more scientifically rigorous investigations are needed. Individuals interested in trying cupping therapy should consult with their healthcare provider and seek treatment from a certified practitioner to ensure safety and proper technique.
As with many traditional therapies, the ultimate test of cupping’s efficacy may lie in further scientific study and an open dialogue between traditional and modern medical practitioners. Meanwhile, those using cupping therapy should weigh the potential benefits against the risks and maintain a critical eye on the treatments they choose to pursue.