Athletes, whether or not professional or leisure, keep in mind that nutrition plays a critical position in their performance, restoration, and overall fitness. The proper food regimen can decorate staying power, power, and pace, whilst the incorrect alternatives can avert development and increase the threat of damage. In this text, we will explore effective nutrition for athletes, not unusual misconceptions, and what would not paintings. Using knowledge of these standards, athletes can optimize their dietary behavior for peak overall performance.
What Works in Nutrition for Athletes
1. Balanced Macronutrients
Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are the primary strength source for athletes. They provide the gasoline needed for both high-depth and staying power activities. Complex carbs like entire grains, results, and veggies have to be the cornerstone of an athlete’s weight loss plan. Easy carbs can be beneficial right now earlier than or after excessive workout routines for quick strength.
Proteins:
Proteins are crucial for muscle restoration and growth. Athletes have to aim for a balanced consumption of lean proteins together with fowl, fish, beans, and legumes. Protein shakes and bars may be handy, but complete meal sources are normally preferred for their extra vitamins.
Fats:
Healthful fats aid hormone production and offer lengthy-lasting strength. Assets consist of avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Athletes should keep away from trans fat and limit saturated fat, focusing instead on unsaturated fat.
2. Timing of meals
Pre-exercise:
Eating a carbohydrate-rich, low-protein lunch 2-3 hours before exercise can improve performance. A smaller snack can be eaten 30-60 minutes earlier than desired.
Put up a workout:
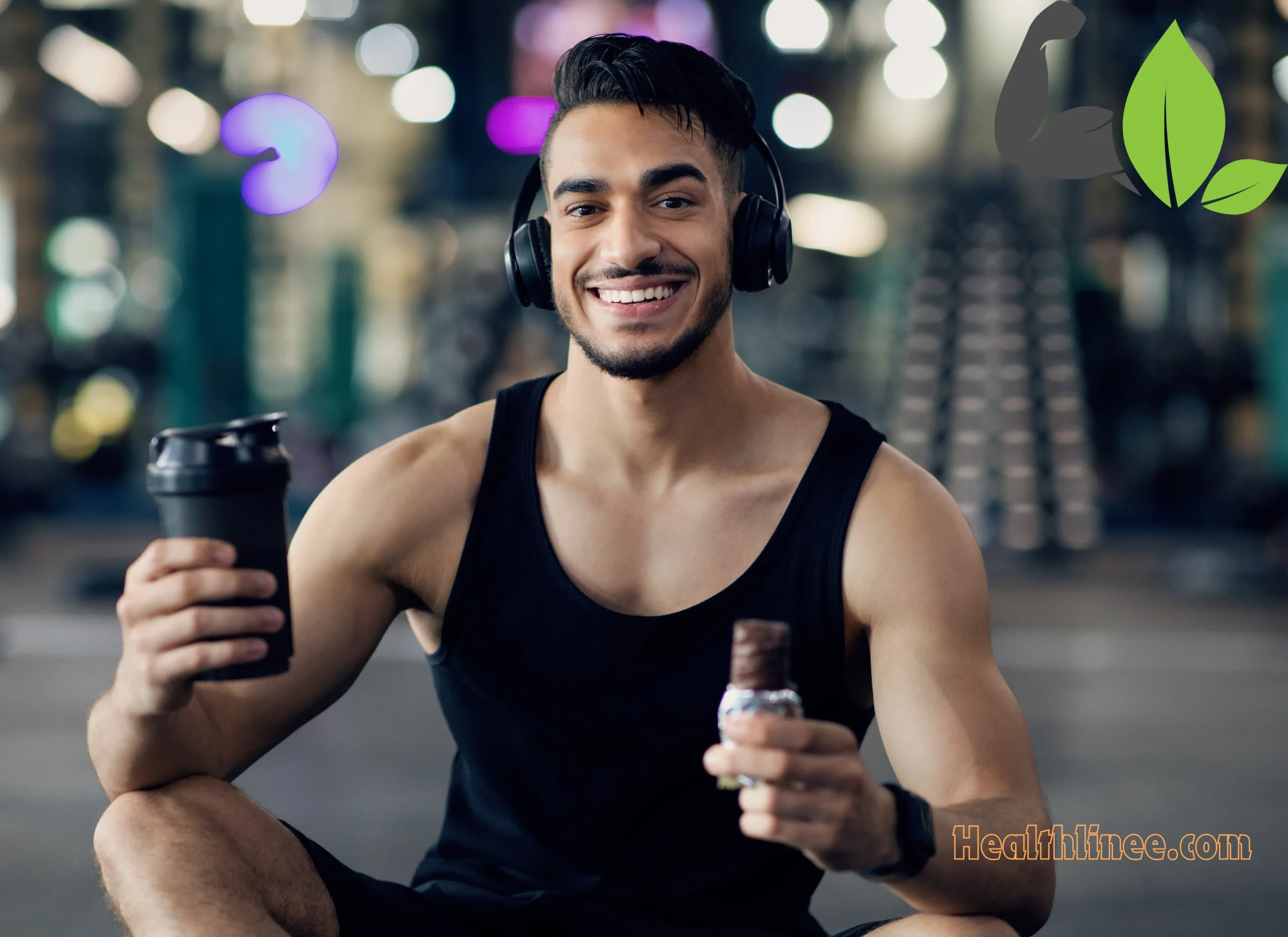
Post-exercise nutrition for athletes is essential for recovery. Consuming protein and carbohydrates within 30 minutes to two hours after exercising can help top off glycogen shops and restore muscular tissues. Chocolate milk, a turkey sandwich, or a smoothie with protein powder and fruit are amazing alternatives.
3. Hydration
Proper hydration is critical for maintaining performance and stopping injuries. Athletes must drink water in the course of the day, no longer simply throughout the workout. Electrolyte-rich drinks are useful for activities lasting more than an hour or in hot conditions to replace misplaced minerals.
4. Micronutrients
Nutrients and minerals play numerous roles in electricity production, immune features, and bone fitness. Athletes have to make sure they eat a ramification of end results and vegetables to get a vast spectrum of nutrients. Unique attention should be paid to calcium, iron, diet D, and antioxidants.
5. Individualization
Because every athlete is different, their dietary needs vary greatly depending on their sport, level of exercise, and metabolism. Working with a sports nutritionist can help customize a healthy diet and weight-loss plan to fit specific objectives and preferences.
What Is the Lack of Artistic Nutrients for Athletes?
1. Overindulgent Diets
Low-Glycemic Meals:
While low-carb diets can effectively reduce weight in certain groups, athletes should generally avoid them. Limiting carbohydrates can cause weariness, decreased performance, and hampered recovery because they are essential for energy.
Fad Diets:
Diets that promise short fixes, which consist of the keto weight-reduction plan or juice cleanses, frequently lack medical backing and may deprive athletes of critical nutrients. The ones diets can cause muscle loss, weakened immune function, and one of a kind fitness issues.
2. Over-reliance on supplements
Supplements can be useful in filling dietary gaps, however they need to no longer replace whole food. Refrain from relying on protein powders, strength bars, and special dietary supplements to avoid imbalances and missing out on the advantages of entire ingredients. Whole foods include fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that may be absent from dietary supplements.
3. Not eating
Athletes’ performance and strength ranges might suffer when they skip meals, especially in the morning. Regular meals and snacks help control blood sugar levels, offer a steady supply of nutrients for muscle repair and recovery, and raise the possibility of injury. Increased nutritional intake is crucial for the production of renewed strength.
4. Ignoring vitamins for restoration
After working out, skipping meals might slow down the body’s ability to rebuild muscle tissue and store glycogen. Ignoring this can lead to chronic pain and poorer-than-average performance in subsequent academic seasons.
5. Loss of fluids
Dehydration can result in cramping in the muscles, a reduction in general performance, and in extreme cases, heat exhaustion or heatstroke. Being thirsty isn’t always an athlete should consistently consume fluids and use their urine’s shade—a moderate yellow is ideal—as a reliable measure of their level of hydration.
Practical advice for athletes
1. Make early plans
Meal planning may help ensure that athletes have a supply of wholesome food and snacks on hand, which will reduce the temptation to choose unhealthy options. Preparing food that is equipped and balanced ahead of time ensures uniformity in the consumption of nutrients and saves time.
2. Listen for your frame
Nutrition for Athletes ought to take note of their bodies’ hunger and fullness cues, as well as how one-of-a-kind meals affect their performance and healing. Preserving a meal journal can assist perceive styles and make vital changes.
3. Stability and range
A numerous weight-reduction plan ensures an extensive range of nutrients. Athletes ought to goal to encompass extraordinary colors and kinds of culmination, greens, proteins, and grains in their meals. This is not the most effective and affords complete vitamins but also maintains food thrilling.
4. Practice self-defense
Athletes can make better nutritional choices if they remain informed about nutrients. Trustworthy resources include medical journals, top-notch websites, and qualified dietitians. Understanding the fundamentals of sports nutrition for athletes can assist in sorting through false information and making informed decisions.
Conclusion
Nutrition is a critical element of an athlete’s training routine. Effective strategies consist of a balanced intake of macronutrients, proper meal timing, good enough hydration, and attention to micronutrients. Personalization is fundamental, as each athlete’s wishes are particular.
Conversely, extreme diets, over-reliance on supplements, skipping food, ignoring restoration nutrients, and dehydration are practices that can restrict athletic performance and ordinary health. Athletes can enhance their long-term well-being, recuperation, and performance by adhering to tried-and-true nutritional guidelines and avoiding frequent mistakes.
By incorporating these tips into daily training, athletes may maintain optimal health, recover more quickly, and perform at their best. The key to achieving of nutrition for athletes success is persistence and determination, just like with any other aspect of training.



Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.